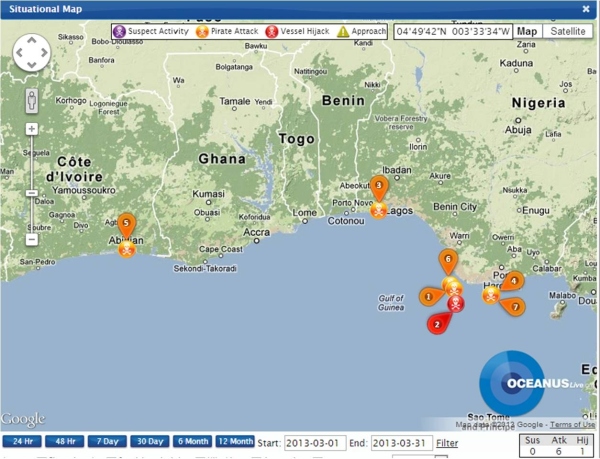
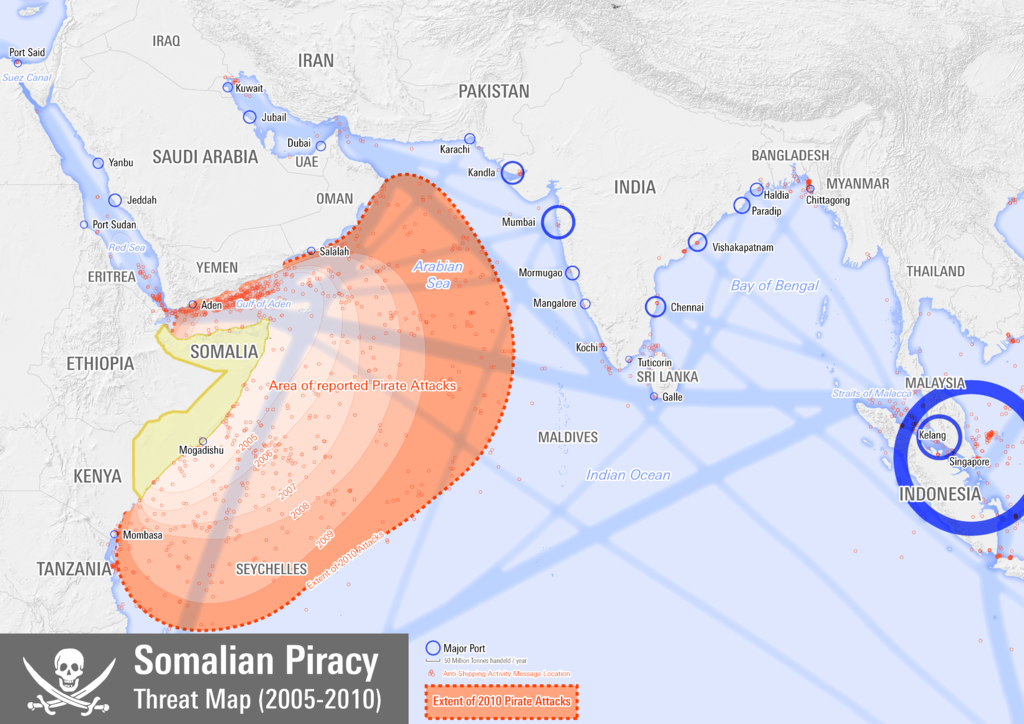
The problem of Piracy become a worldwide issue at the beginning of 21st century. The deteriorating security situation in the seas off Somalia, the Gulf of Aden and the wider Western Indian Ocean between 2005 and 2012 and also the increasing number of attacks in the Gulf of Guinea are a major problem.
Some measures had been taken by the UN Security Council, such as unanimously passed declaration authorizing nations that have the consent of the Transitional Federal Government to enter Somali territorial waters to deal with pirates. What is more a Russian drafted resolution was established on 27 April 2010. It called on all states to criminalise piracy and suggested the possibility of establishing a regional or international tribunal to prosecute suspected pirates.
The idea of piracy should be condemned as a whole, as it is an illegal, unjustifiable means to achieve any kind of goal. The best way to combat piracy in Somalia, at the Gulf of Aden, and the Somali Basin, as well in the coast of West Africa and everywhere else, is to eliminate the causes that are at the base of it. It is believed that dumping toxic refuse in Somali waters by foreign ships is the origin of the problem. The contamination of water constrained the ability of local fishermen to earn a living. The natives started to attack vessels in order to flush them. However it quickly become an easy way to make money by robbing and collecting ransoms for abducted members of the crew.

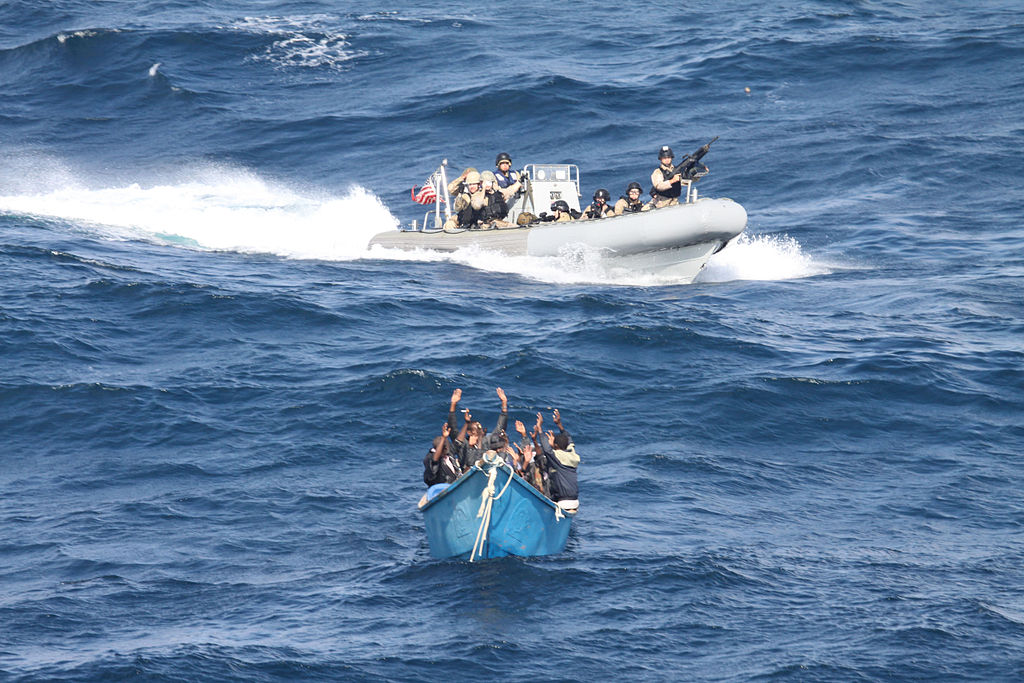
Another solution for the concern is the establishment of regional cooperation among States. It has an important role in solving the problem of piracy and armed robbery against ships, as proven by the success of the regional anti-piracy operation in the Straits of Malacca and Singapore for example. Nevertheless the vast sea area in which the pirates now operate makes it difficult to patrol and monitor effectively, especially with the limited resources available. More resources, in the form of naval vessels and aircrafts are needed. But also it is crucial to constantly cooperate with the International Maritime Organization.

Some of the countries on the UN proceedings also supported the creation of a UN military force, under the control of the IMO, to strike down, disband and arrest pirates. Furthermore the creation of an international court to try pirates acting internationally. Also Germany reminded the international community that the trial of any offender, criminal, pirate or terrorist has to follow the law and must not violate human rights. And that the troops will not be put ashore and any actions will be limited to support activities close to where suspect ships are moored.
Hopefully, by setting a common framework to combat piracy and by creating an international legislation and an international force to enforce the framework, the threat of piracy in Horn of Africa and West Africa will greatly diminish.
Maria Majszyk
Based on a presentation for Rasz MUN 2014 conference.